Although it doesn’t look like, the white fly is a very dangerous pest to your plants…


It is very hard to eradicate.

It is around 2 mm in length.
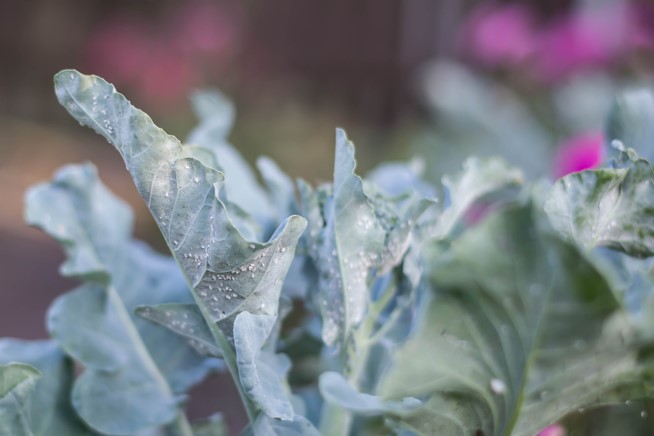




It suck liquids out of the plant’s leaves and secrete sticky material called honeydew.

Black mold grows on the honeydew, which slows down the photosynthesis of the plant.


But the main damage is done by the 100 different kinds of viruses it can carry, and transfer, into the plants, while zipping the plants fluids.



These viruses cause growing disorders and distorted plants and fruits.
Usually, the plants stop growing and stop yielding fruits.
Once the virus is inside the plant, the plant is doomed.
Nothing can be done about it.
There is no remedy.
It’s better to uproot such a plant and throw it away, because the virus will multiply inside it,
and the plant will become a source through which other plants could be infected.





One of the solutions needed to be taken is to grow your plants inside greenhouses with 50 mesh type nets.




The whitefly cannot go through this type of net.

It is recommended to use at least 3 kinds of different pesticides,
and alternate between them every 4 days, in order to overcome pest’s resistance,
and completely exterminate them.
For further information about this, read this post , and this post also.
There are 3 ways to eliminate whiteflies: chemical, organic and biological.
Chemical:
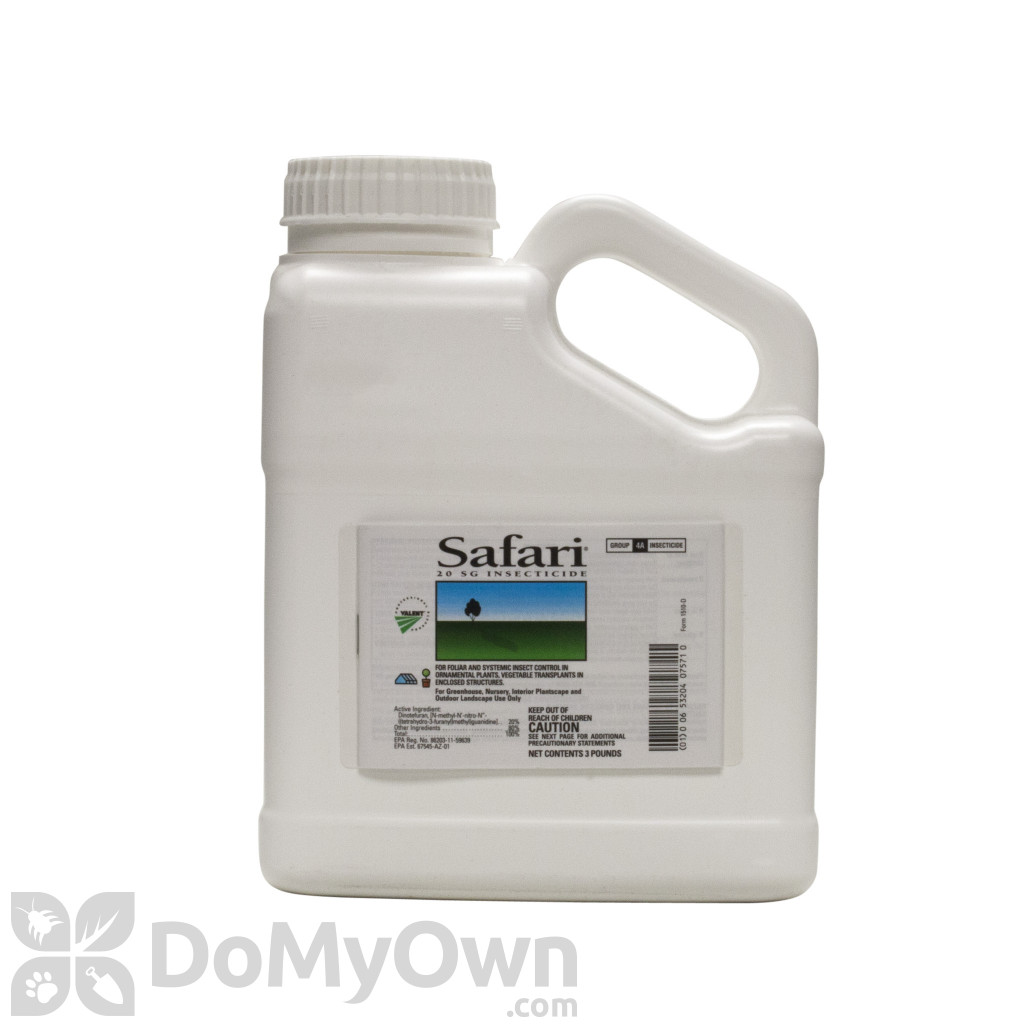
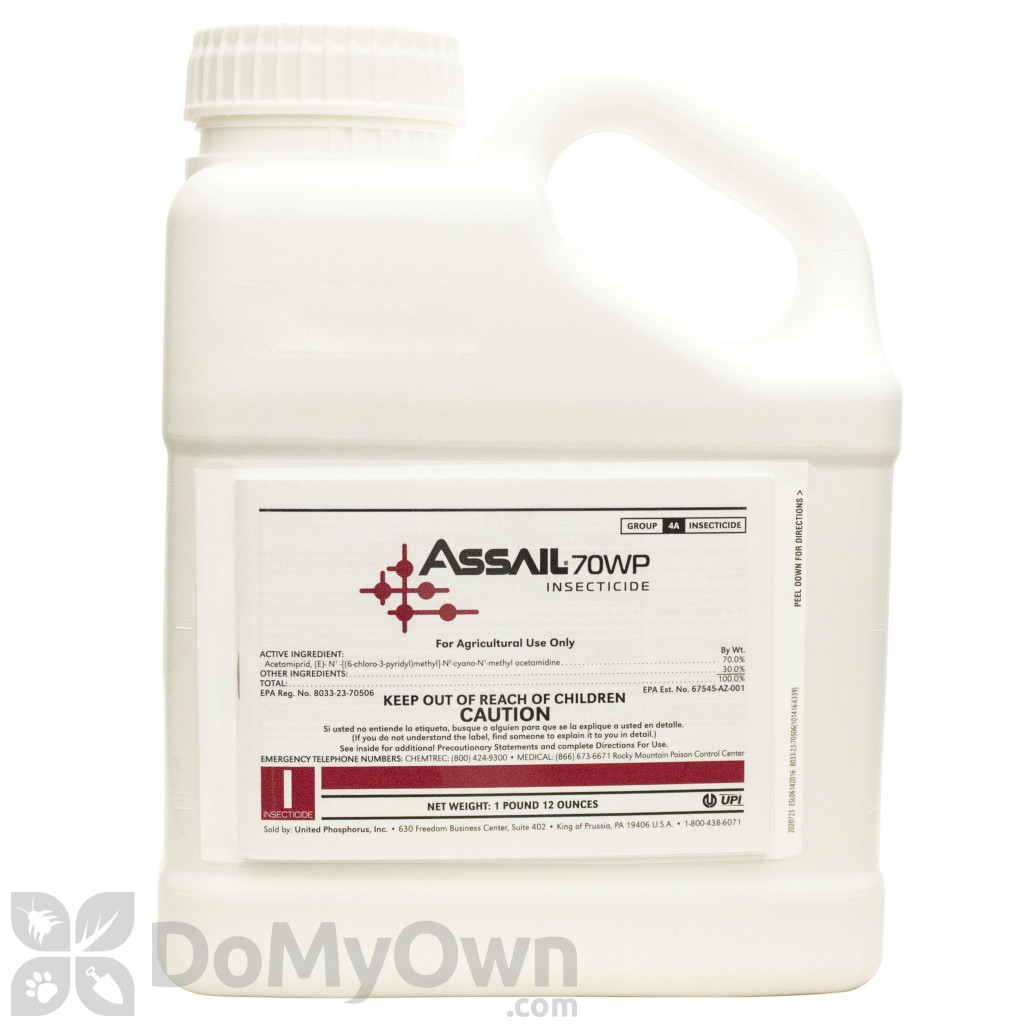
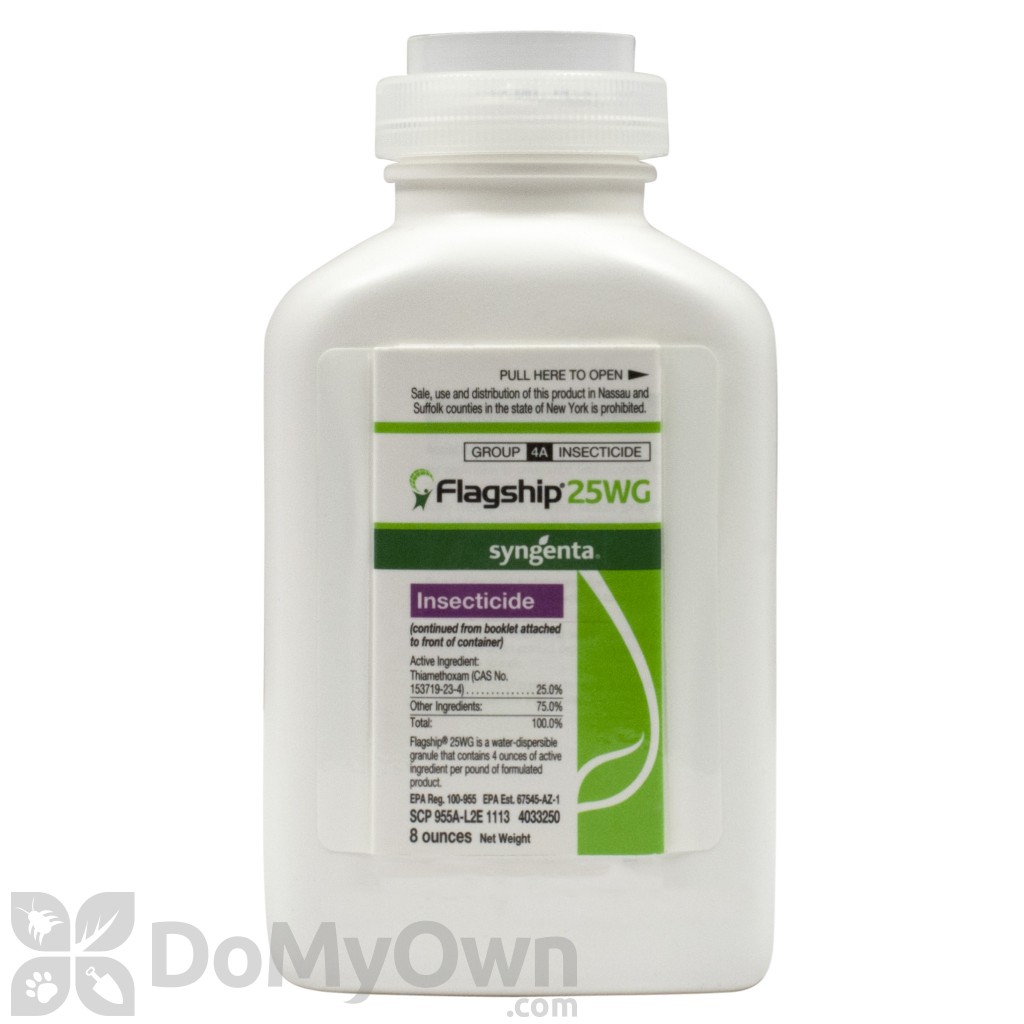
Best pesticides for whitefly,
Active ingredients:
Organic:
Azadirachtin–
Extracted from the neem tree, it is the active ingredient here.
Insects are repelled by it’s taste and smell, and it is also works as a molting/growth disruptor.
This insect growth regulator (IGR) disrupts the life cycle between larval, pupal and nymphal stages.

Beauveria bassiana–
Live fungal spores for the control of soft-bodied insects in organic production.
Its spores adhere to the target insect’s outer shell, and begin the infection process.
At this point, you may notice insects with a whitish appearance.
Once the spores have breached the protective barrier of the outer shell, they continue to multiply until they reach the insect’s blood, which they begin feeding on.
Death occurs 7 to 14 days after infection.

Insect netting


Neem oil
A naturally occurring pesticide, found in seeds from the neem tree.
Azadirachtin is the most active component here.
It reduces insect feeding and acts as a repellent.
It also interferes with insect hormone systems, making it harder for insects to grow and lay eggs.

Paraffinic Oil
acts as a smothering and prevents insect respiration.
For maximum effectiveness, spray all kinds of oils well, especially on the underside of the leaf.
The foliage of the crop should be well moistened.
Spray in the cool evening hours.
It is recommended to spray two consecutive sprays three days apart.

Mineral Oil
Covers the egg, larvae, nymph and adult stages, causing suffocation.
It leaves no toxic residue on plants.

Pyrethrin
A collection of six esters, which are found in high concentrations within the achenes of the flower.
It targets insects’ nervous systems.
Pyrethrin induce excited behavior in the insect, which results in increased insect exposure to the pyrethrin and eventual death.

Biological:
Amblyseius swirskii-

An excellent beneficial mite for preventative control of whitefly.
It can consume about 10 whitefly larvae a day, and up to about 20 whitefly eggs per day.
This beneficial insect can survive by consuming pollen and mold also.
Best used early in crop/pest cycle to prevent whitefly buildup, since it does not feed on adult stages.
Biological beneficials have a very short life expectancy and therefore need to be introduced into the crop as soon as possible after receipt.
Failure to do so can have a negative impact on their quality.

You might also like these articles:
- How to Combat Pests During Growing Season: The Importance of Using Multiple Pesticides to Prevent Resistance and Maximize Yield
- How to differentiate between pesticides
- How to find your pesticide in a store
- The Ultimate Guide to Eradicating Spider Mites
- Protect Your Plants from Whitefly Infestation and Virus with These Tips!
- How to Control Aphids: Chemical, Organic, and Biological Methods for Effective Pest Management
- Combatting Thrips: Effective Strategies for Eliminating and Controlling Pest Infestations
- Effective Ways to Control Leaf Miners: Chemical, Organic, and Biological Treatments
- Tuta absoluta Moth: Prevention and Control Methods for Tomato and Eggplant Farmers
- A Comprehensive Guide to Caterpillar Pest Control
- Maximizing Efficiency: How to Combine Pesticides to Control Multiple Crop Pests with One Spray
- Vegetable garden sprayer