Weeds can quickly invade lawns and garden beds, choking out desirable plants and lowering the aesthetic value of the landscape.
The use of herbicides can be an effective way to control and eliminate weeds.
In this article, we will look at some of the most common weeds found in lawns and gardens, as well as the herbicides that are effective in controlling them.
From dandelions to wild onion, understanding how to control these pesky plants can help homeowners and gardeners maintain a healthy and vibrant outdoor space.
Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale):
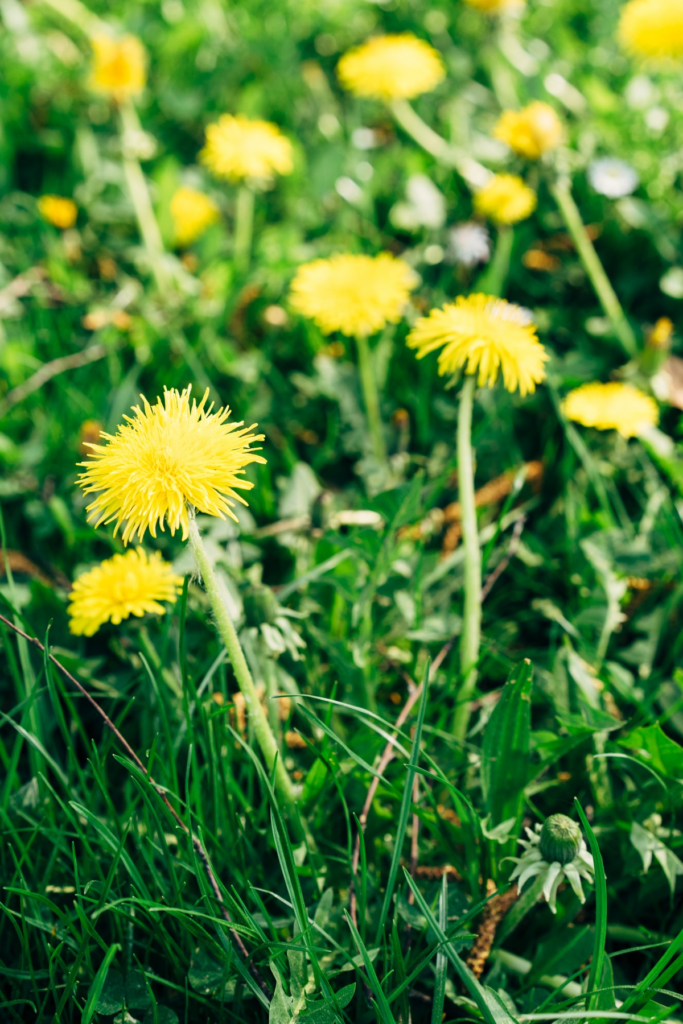

A common perennial weed with deep taproots that produce yellow flowers.
Effective herbicides for controlling dandelions include 2,4-D, dicamba, and MCPP.

Crabgrass (Digitaria spp.):
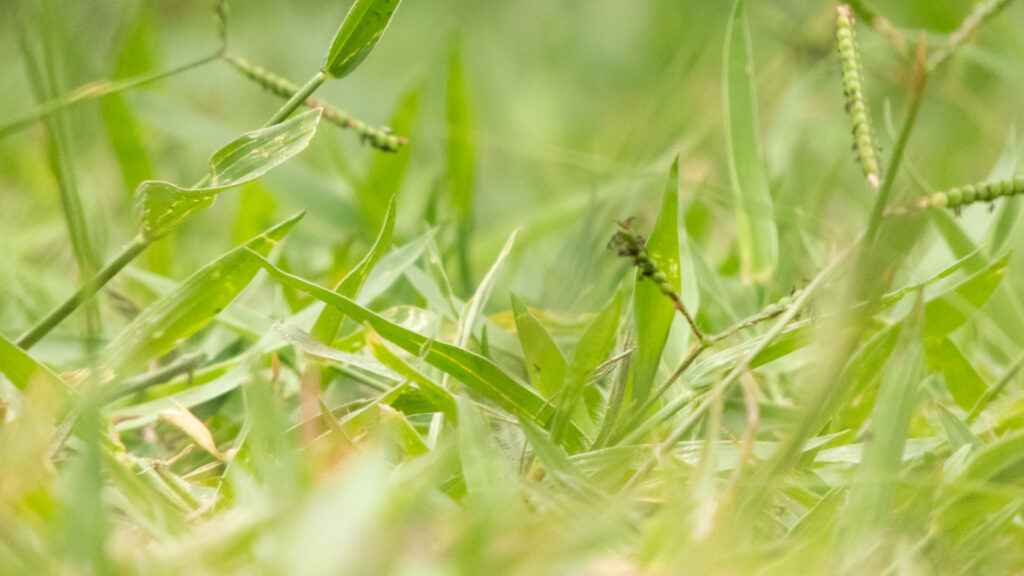

A summer annual grass that spreads by seed and can quickly invade turf areas.
Herbicides such as mesotrione, quinclorac, and dithiopyr are effective in controlling crabgrass.


Common chickweed (Stellaria media):
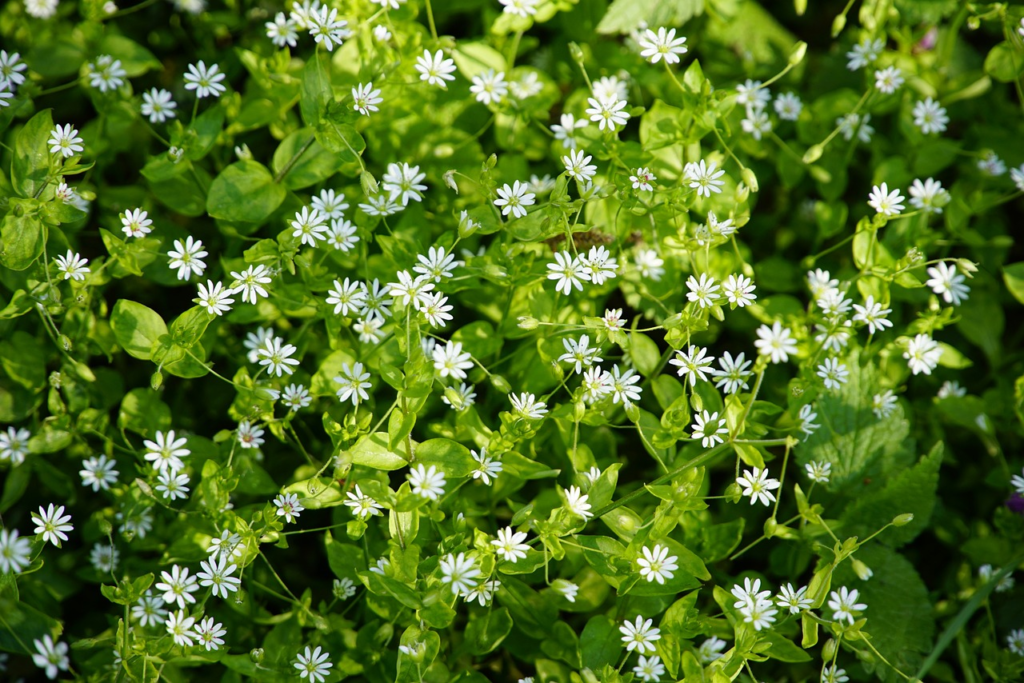

A cool-season annual weed with small white flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as dicamba, 2,4-D, and triclopyr are effective in controlling chickweed.
Clover (Trifolium spp.):
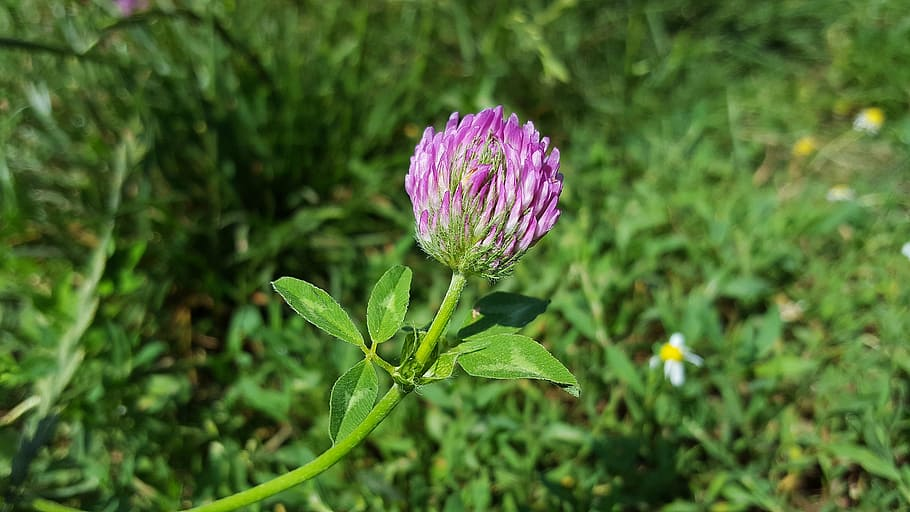

A perennial weed that produces white or pink flowers and can be found in lawns, gardens, and fields. Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and MCPA are effective in controlling clover.
Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense):
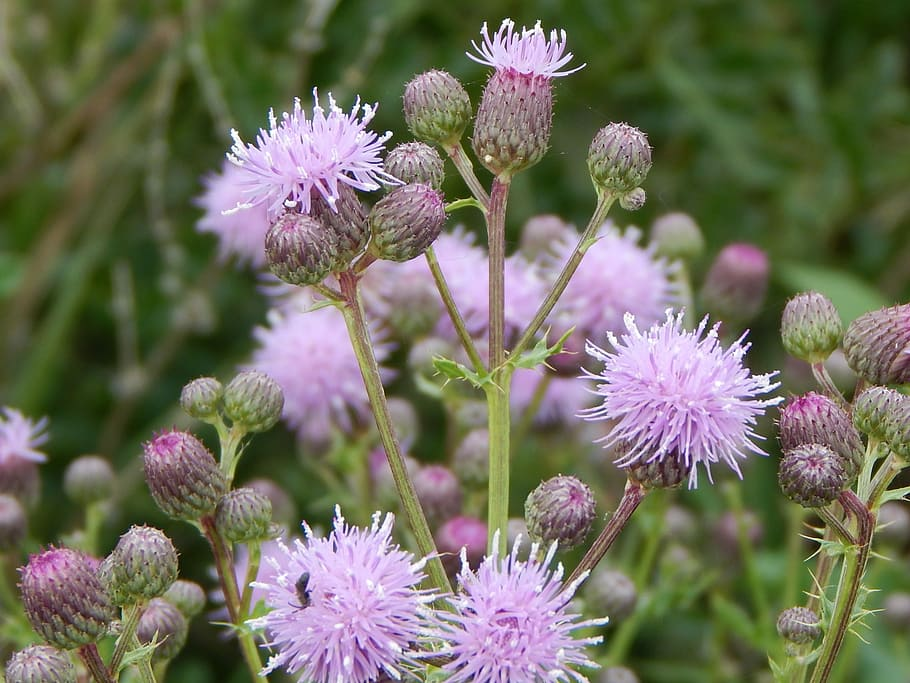

A perennial weed, that spreads by underground roots and produces purple flowers.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, dicamba, and 2,4-D are effective in controlling Canada thistle.
Bindweed (Convolvulus arvensis):
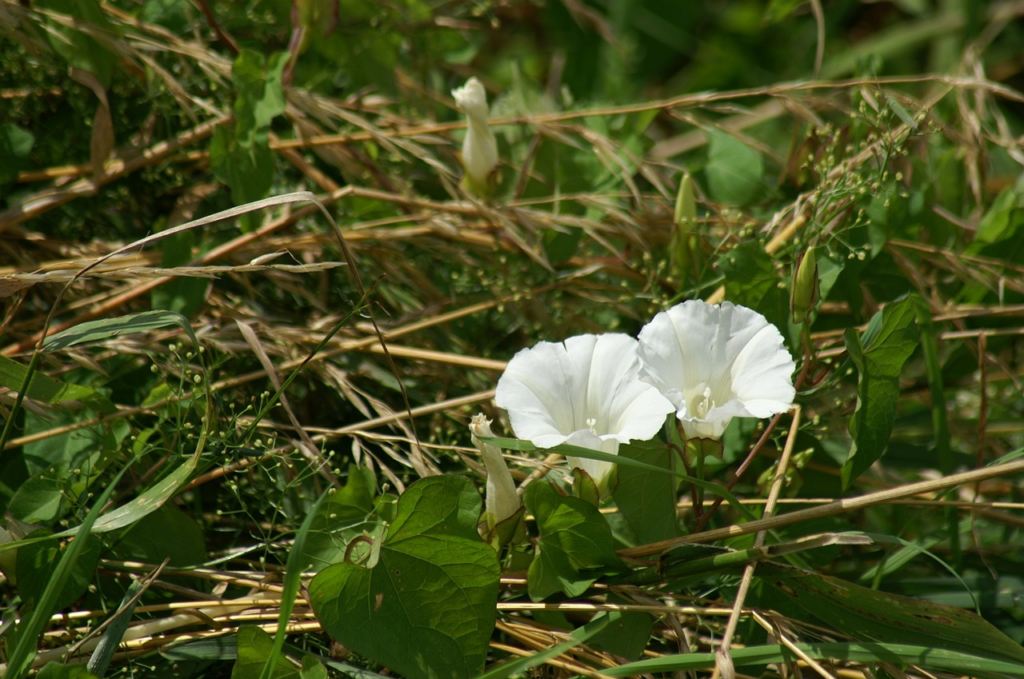

A perennial weed with long vines that can smother other plants.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, dicamba, and 2,4-D are effective in controlling bindweed.
Plantain (Plantago spp.):
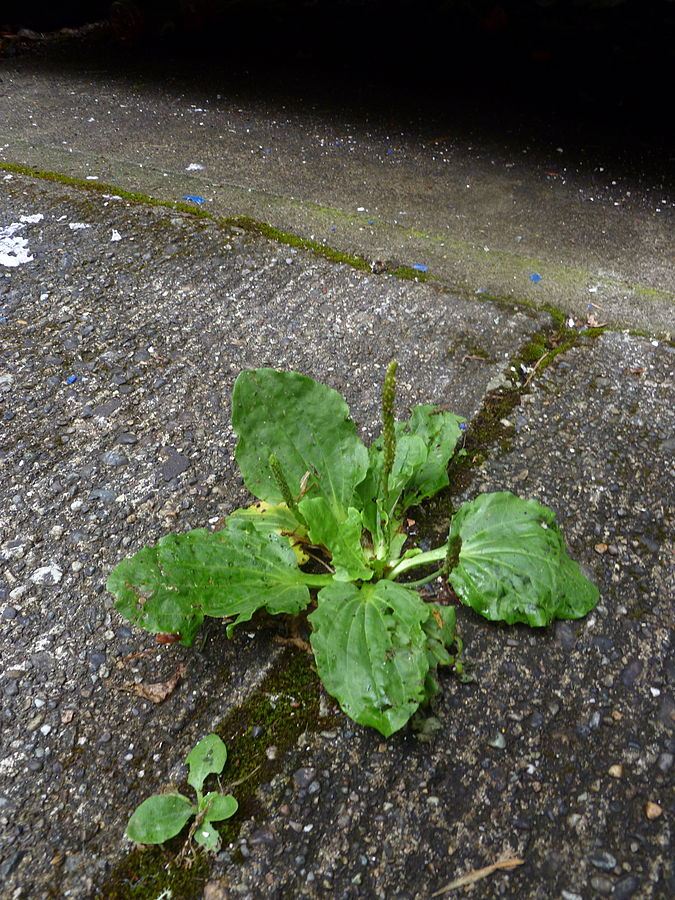

A common broadleaf weed that can be found in lawns, gardens, and fields.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and triclopyr are effective in controlling plantain.

Purslane (Portulaca oleracea):
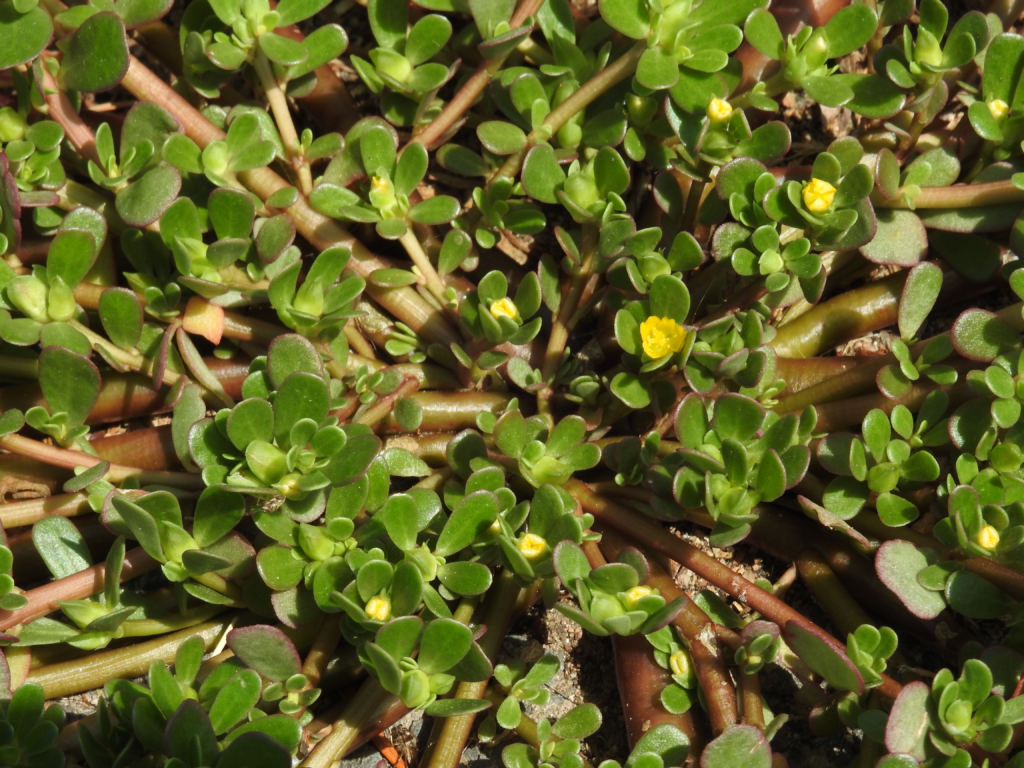

A summer annual weed with succulent leaves and pink or yellow flowers.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, dicamba, and 2,4-D are effective in controlling purslane.
Poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans):
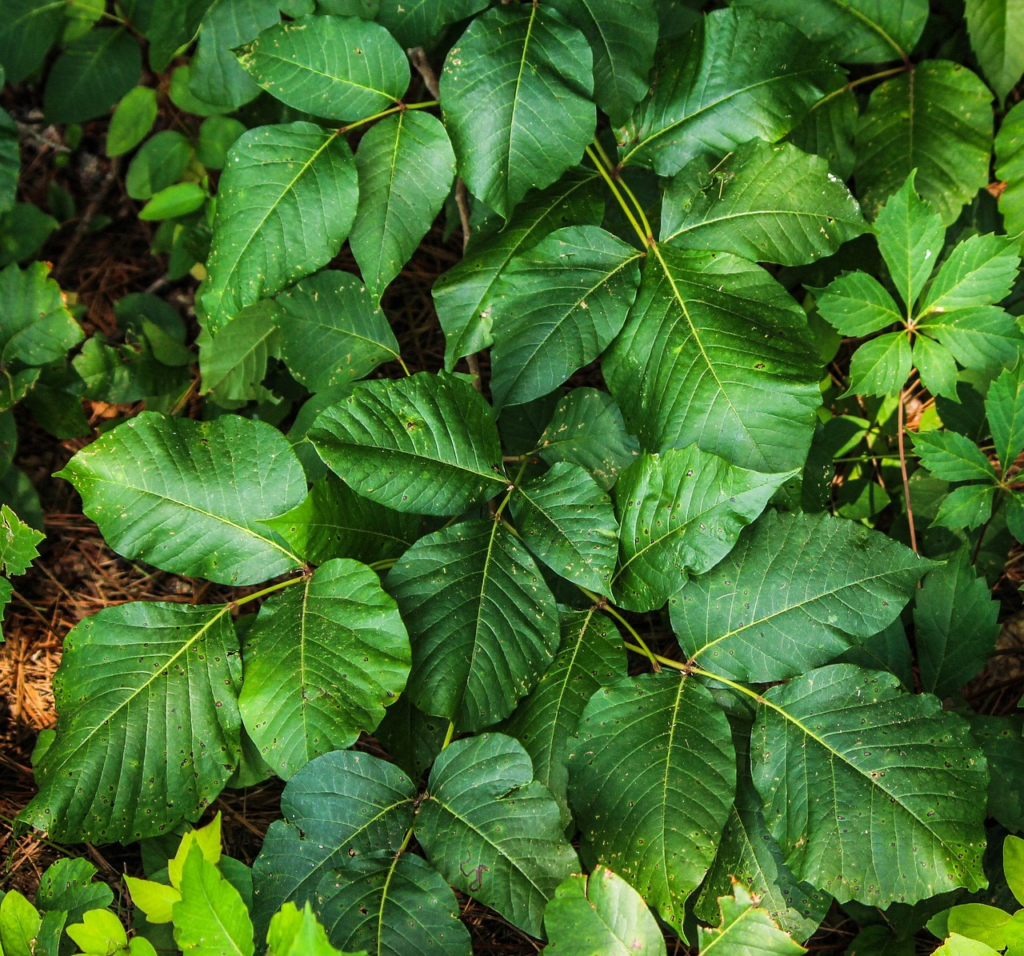

A perennial vine with three shiny green leaves that can cause a rash.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, triclopyr, and imazapyr are effective in controlling poison ivy.

Pigweed (Amaranthus spp.):
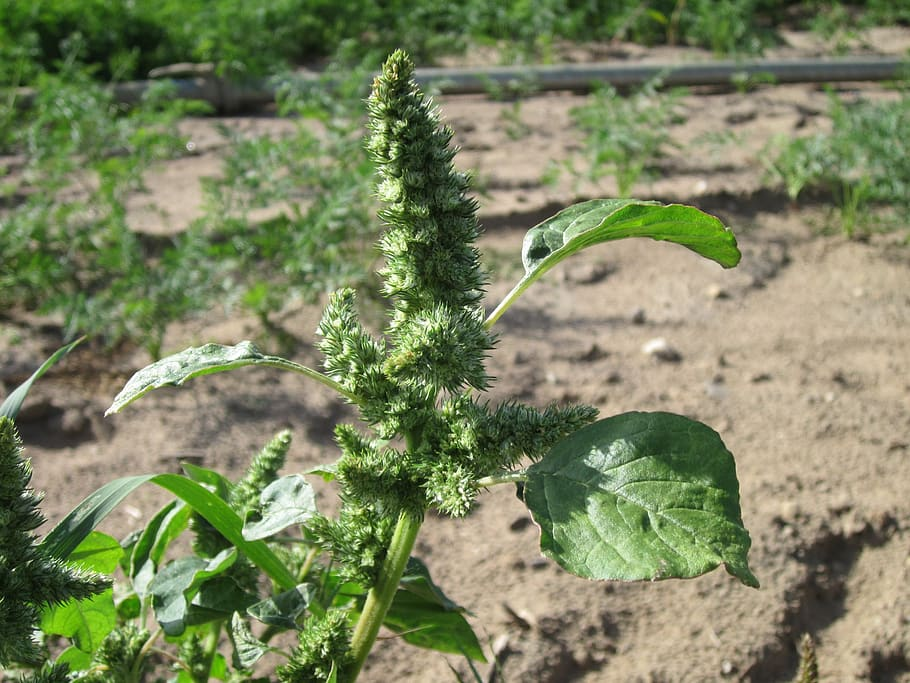

A summer annual weed that can grow up to six feet tall and produces tiny flowers.
Herbicides such as atrazine, mesotrione, and dicamba are effective in controlling pigweed.

Nutsedge (Cyperus spp.):
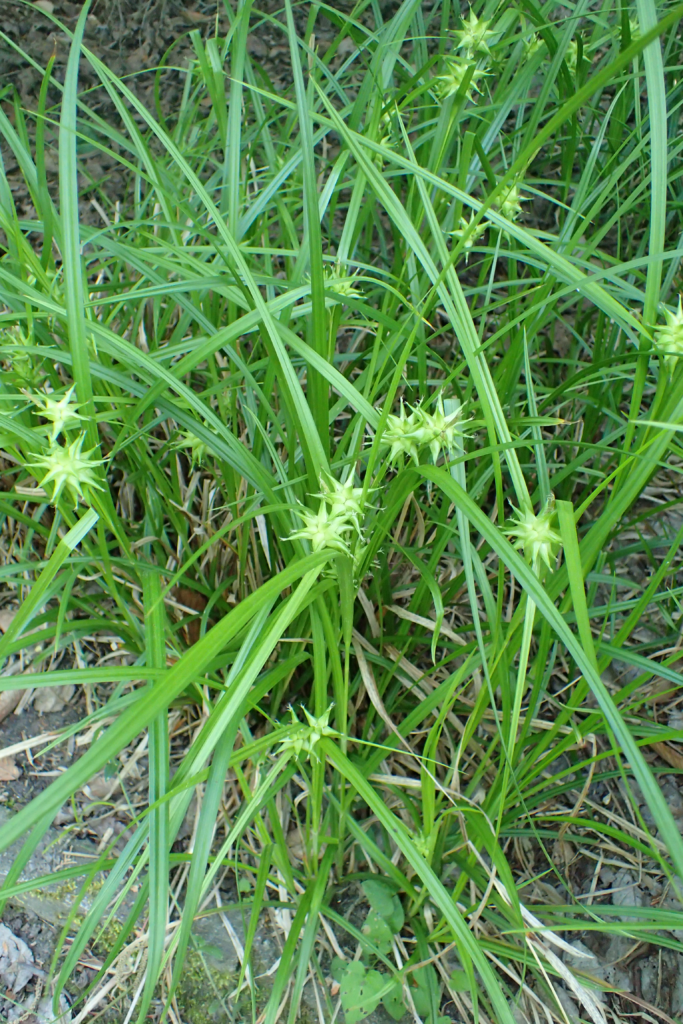

A perennial grass-like weed with triangular stems that can be difficult to control.
Herbicides such as halosulfuron-methyl, sulfentrazone, and imazaquin are effective in controlling nutsedge.


Henbit (Lamium amplexicaule):
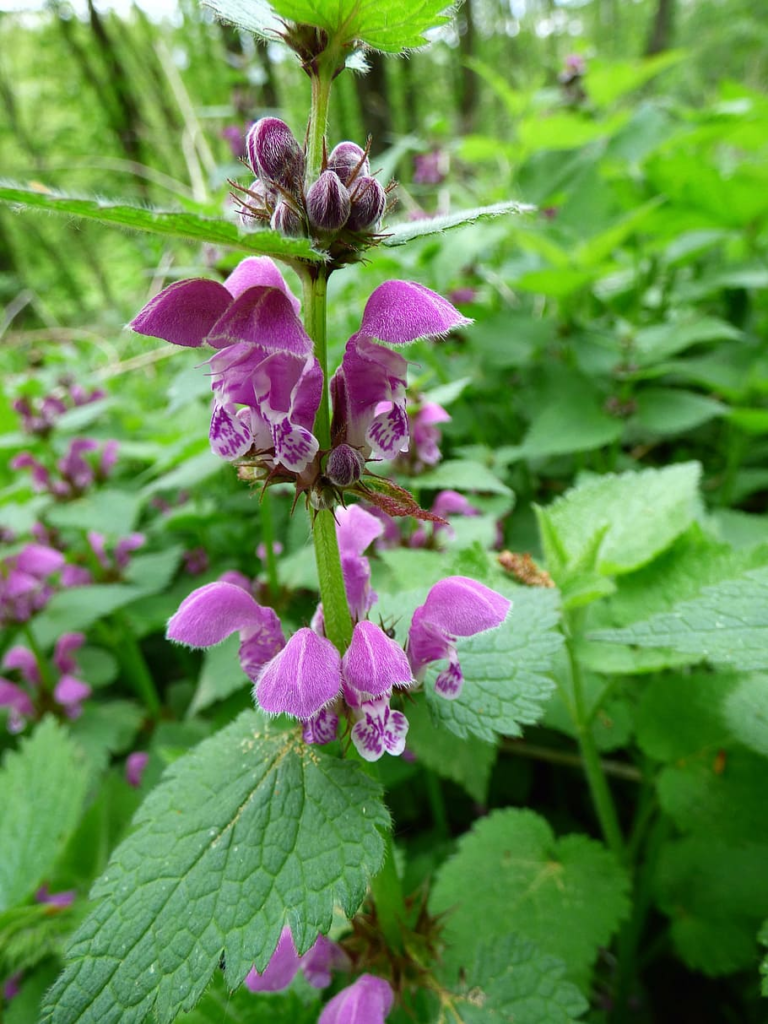

A cool-season annual weed with small purple flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds. Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and triclopyr are effective in controlling henbit.
Japanese knotweed (Fallopia japonica):
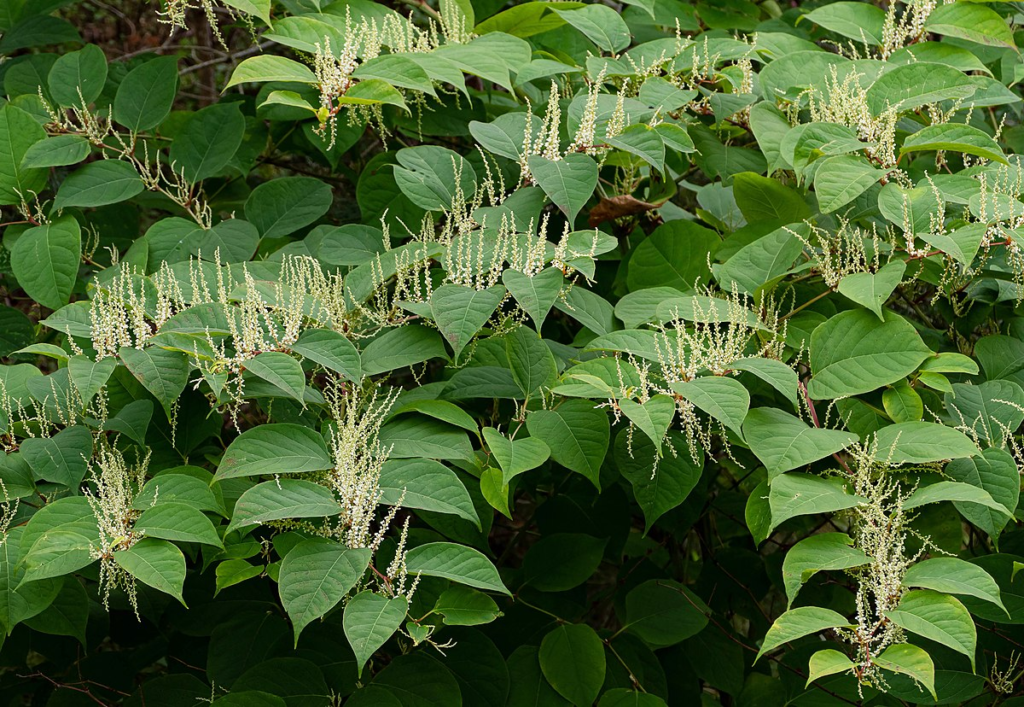

A perennial weed with bamboo-like stems that can grow up to 10 feet tall.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, triclopyr, and imazapyr are effective in controlling Japanese knotweed.
Yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus):
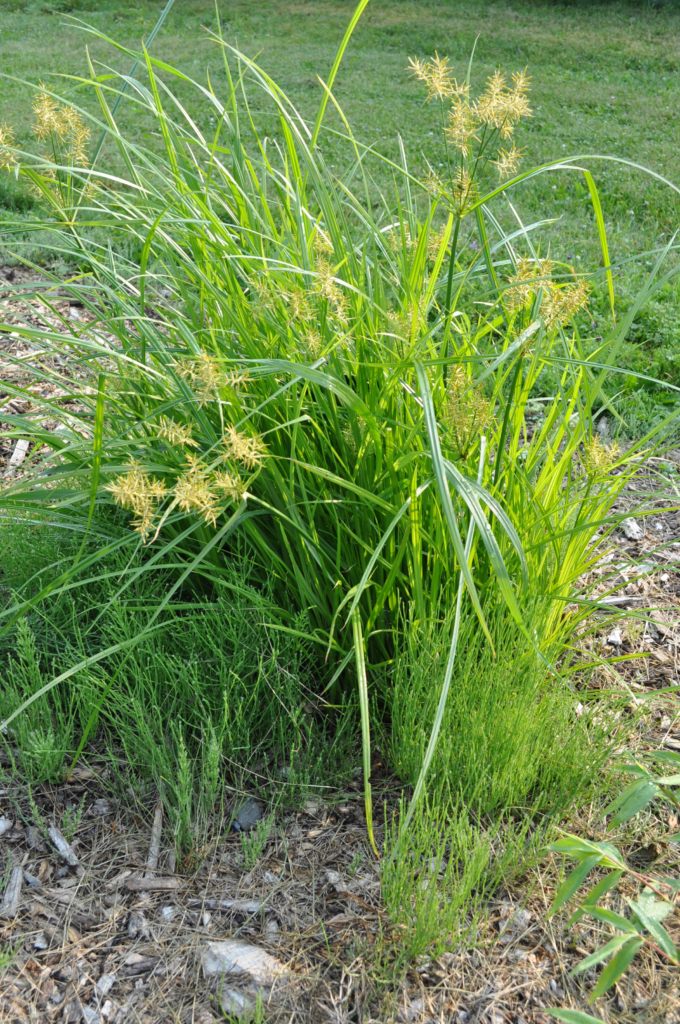

A perennial weed with yellow-green leaves and triangular stems that can be difficult to control.
Herbicides such as halosulfuron-methyl, sulfentrazone, and imazaquin are effective in controlling yellow nutsedge.
Wild violet (Viola Sororia):
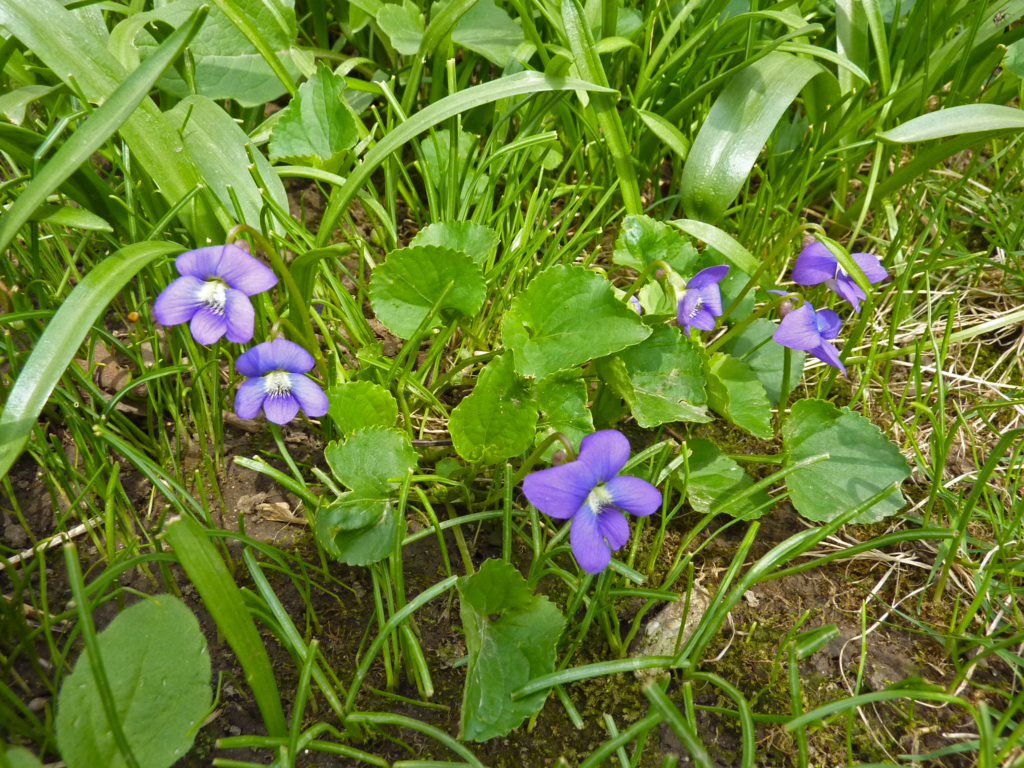

A perennial weed with heart-shaped leaves and purple flowers.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and triclopyr are effective in controlling wild violet.
Broadleaf plantain (Plantago major):
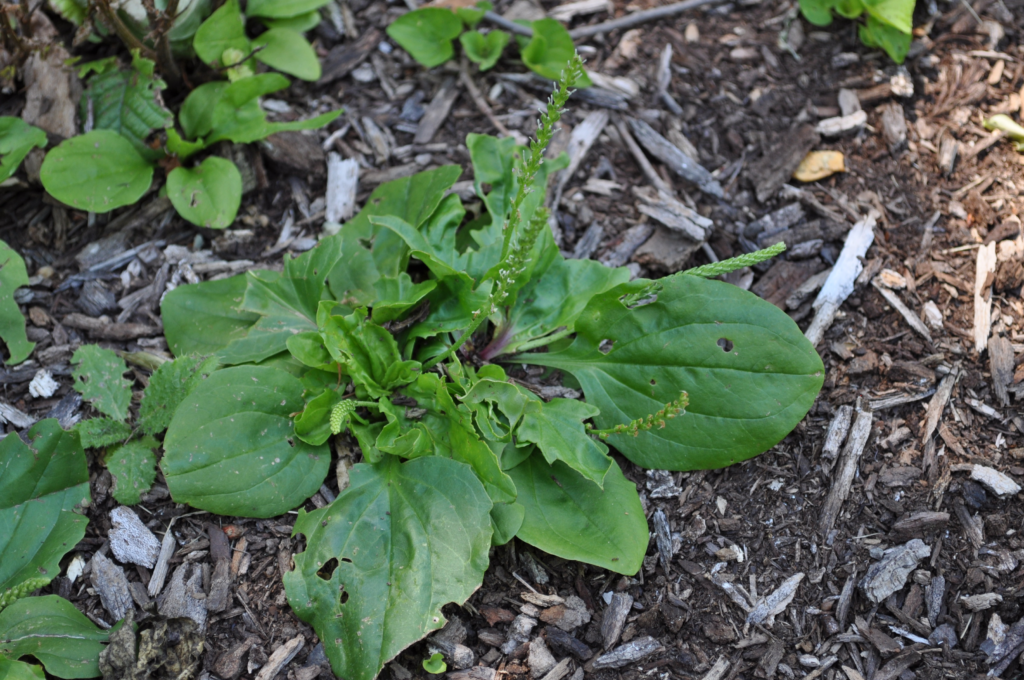

A common broadleaf weed that can be found in lawns, gardens, and fields.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and triclopyr are effective in controlling broadleaf plantain.
Black medic (Medicago lupulina):
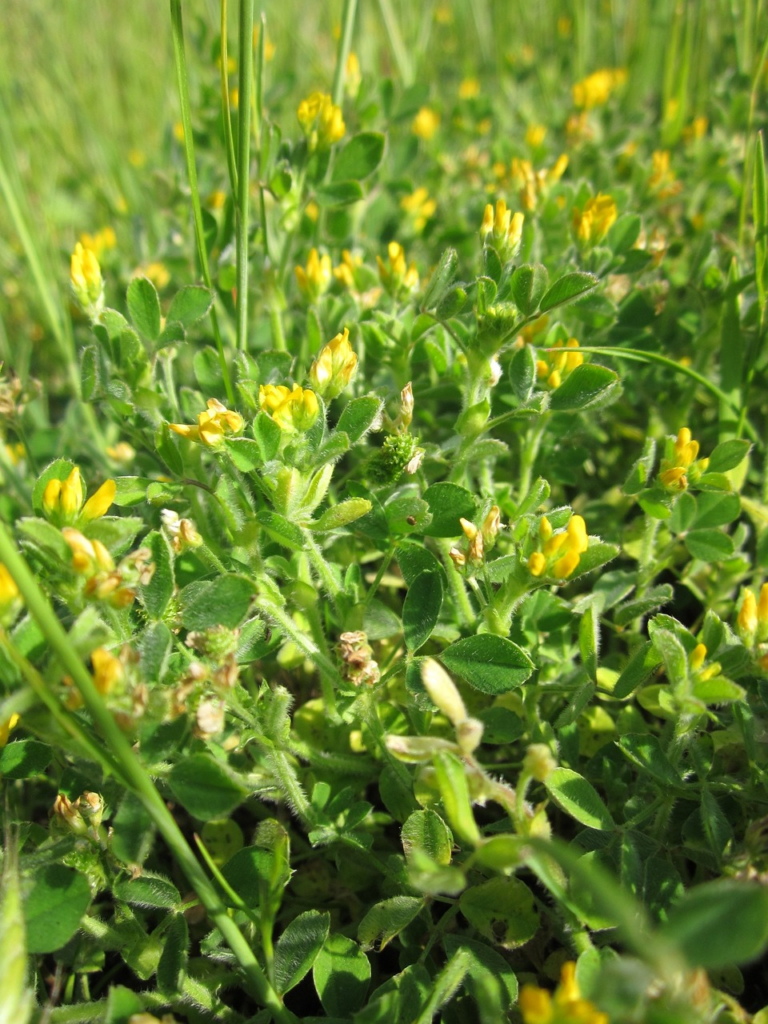

A cool-season annual weed with yellow flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and triclopyr are effective in controlling black medic.
Common groundsel (Senecio vulgaris):
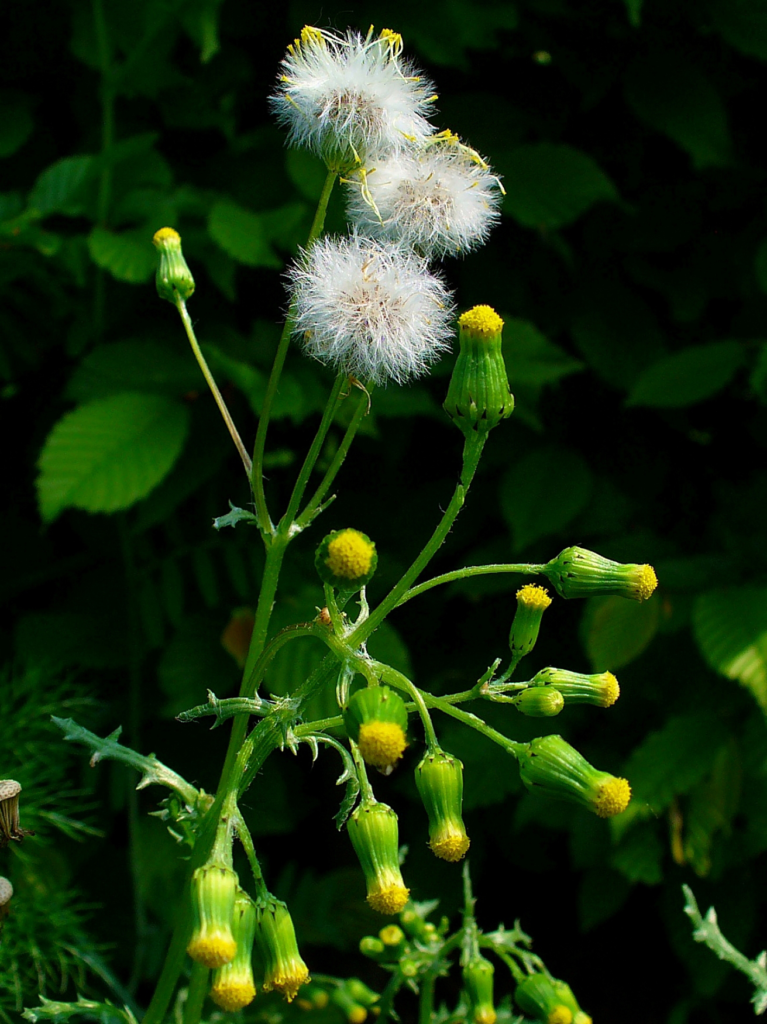

A cool-season annual weed with yellow flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and triclopyr are effective in controlling common groundsel.
Knotweed (Polygonum spp.):
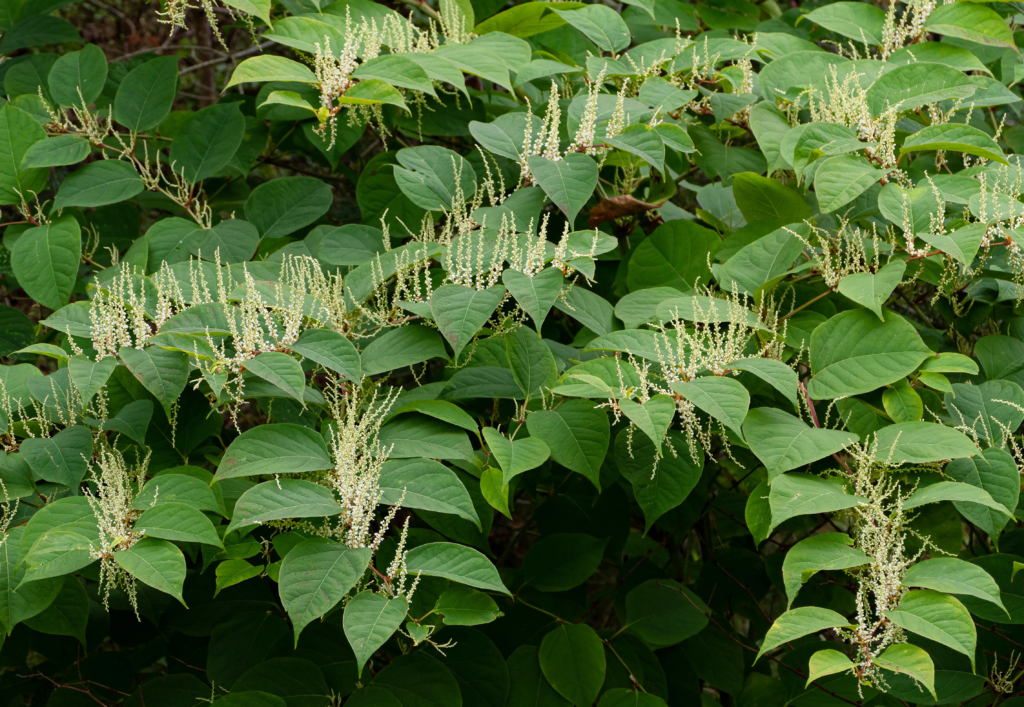

A perennial weed with a thick root system that can be difficult to control.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, triclopyr, and imazapyr are effective in controlling knotweed.
Ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia):
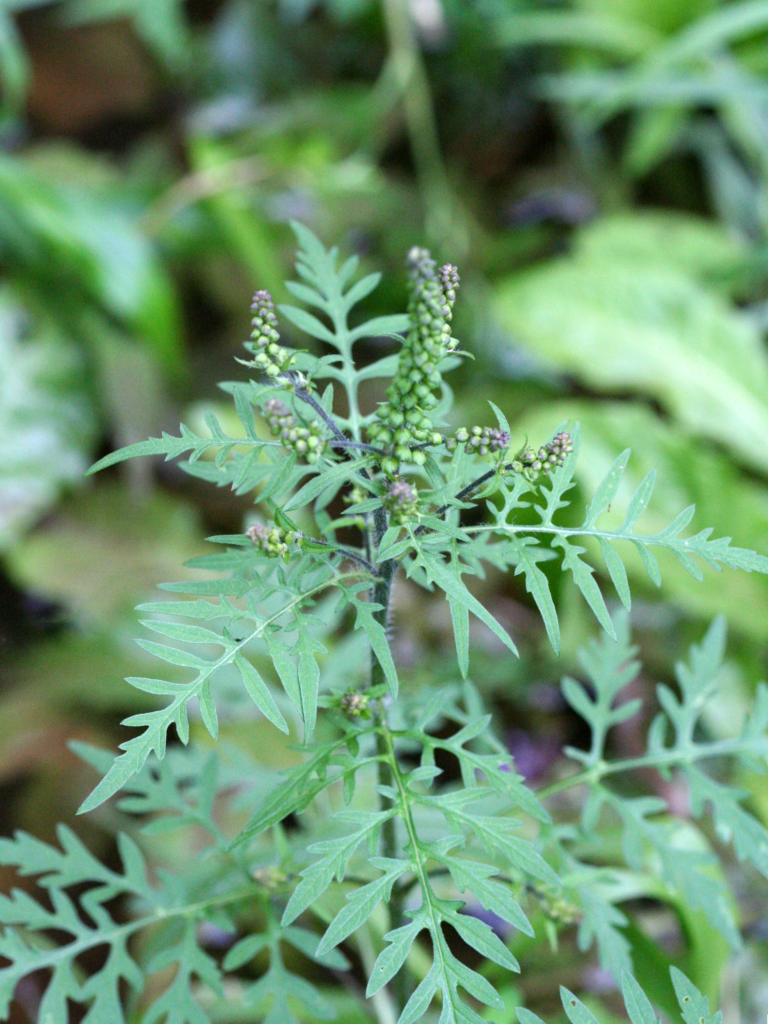

A summer annual weed with green flowers that can cause allergies.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and glyphosate are effective in controlling ragweed.
Spurge (Euphorbia maculata):
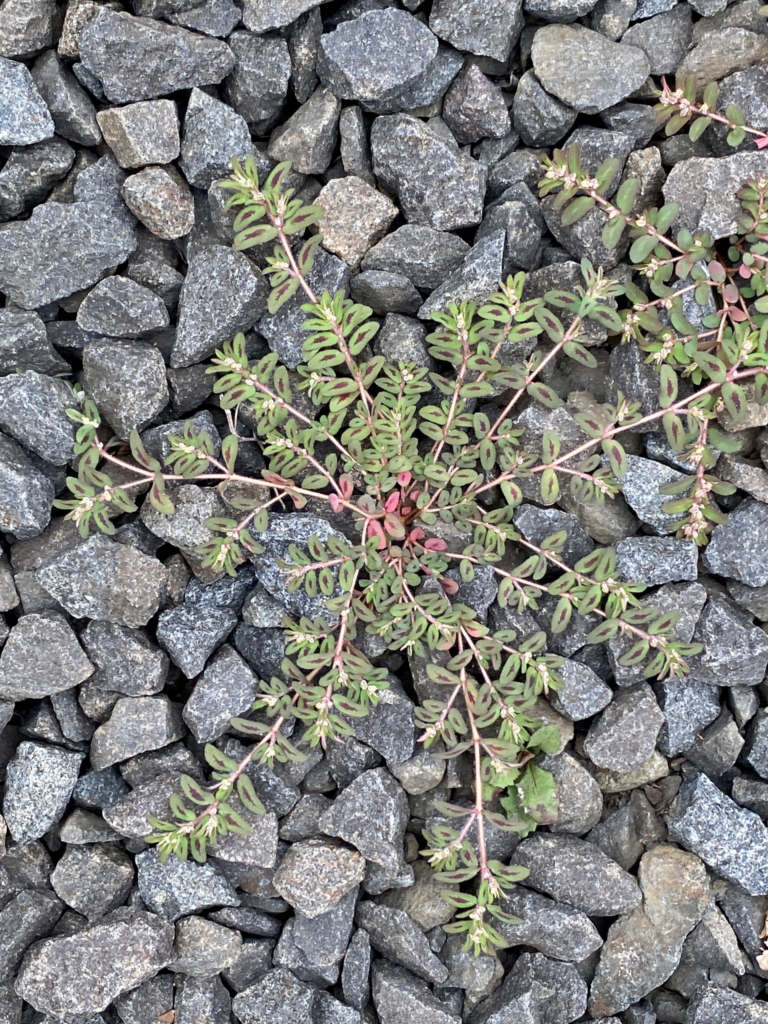

A summer annual weed with milky sap that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and glyphosate are effective in controlling spurge.
Wild garlic (Allium vineale):

A perennial weed with a strong odor that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, 2,4-D, and dicamba are effective in controlling wild garlic.
Wild onion (Allium canadense):
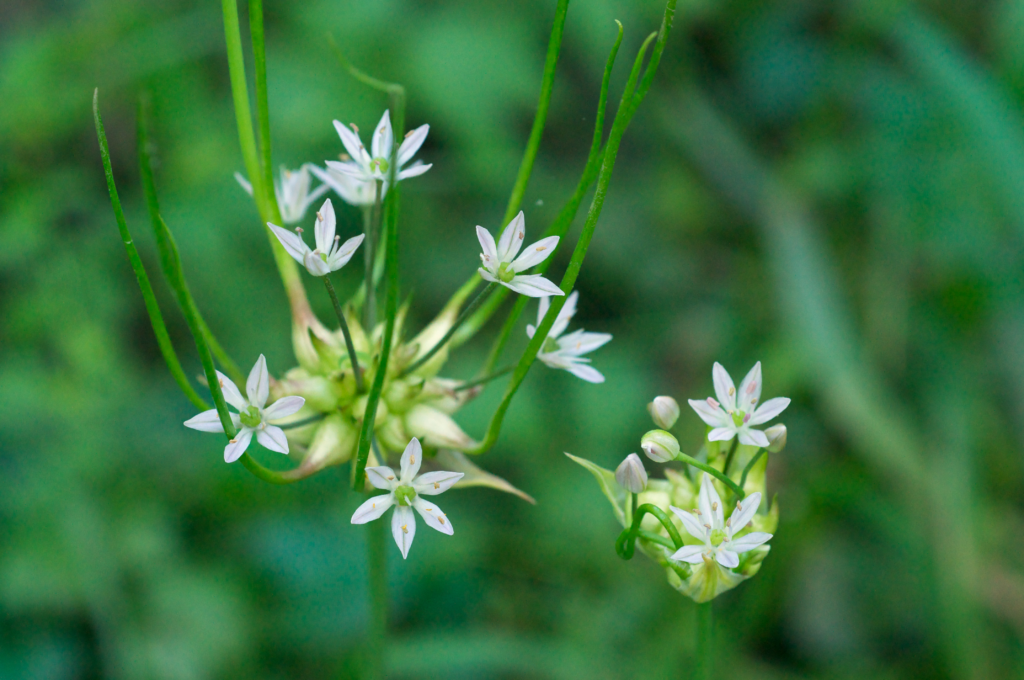

A perennial weed with a strong odor that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, 2,4-D, and dicamba are effective in controlling wild onion.
Yellow rocket (Barbarea vulgaris):
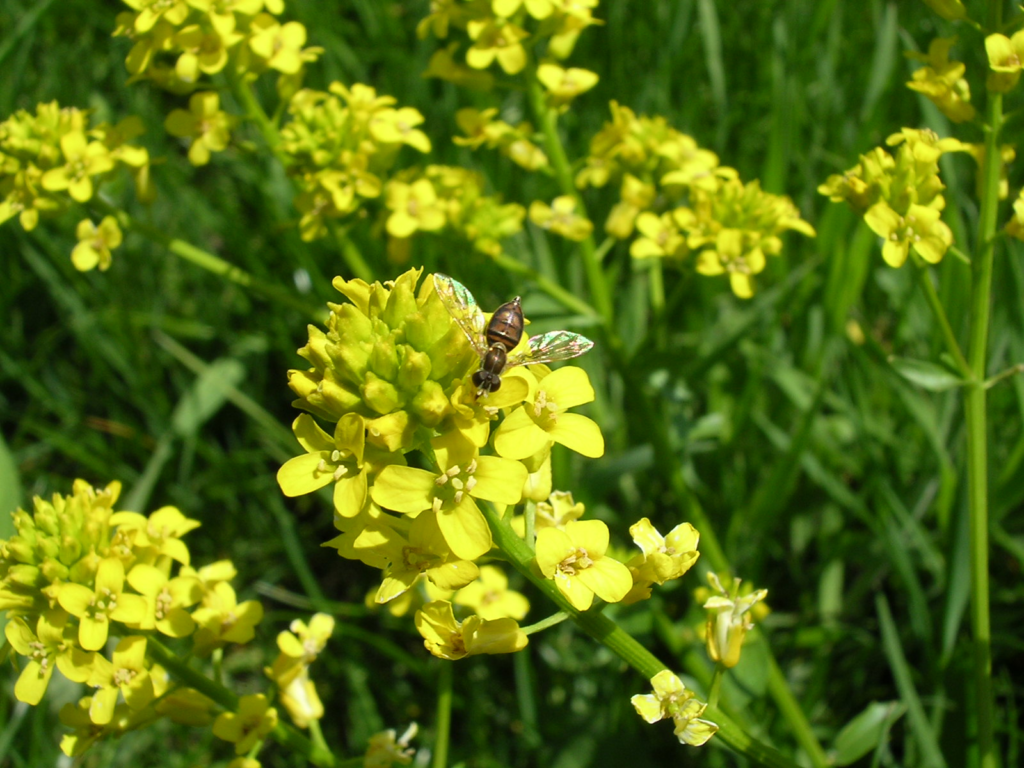

A cool-season annual weed with yellow flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and triclopyr are effective in controlling yellow rocket.
Carpetweed (Mollugo verticillata):
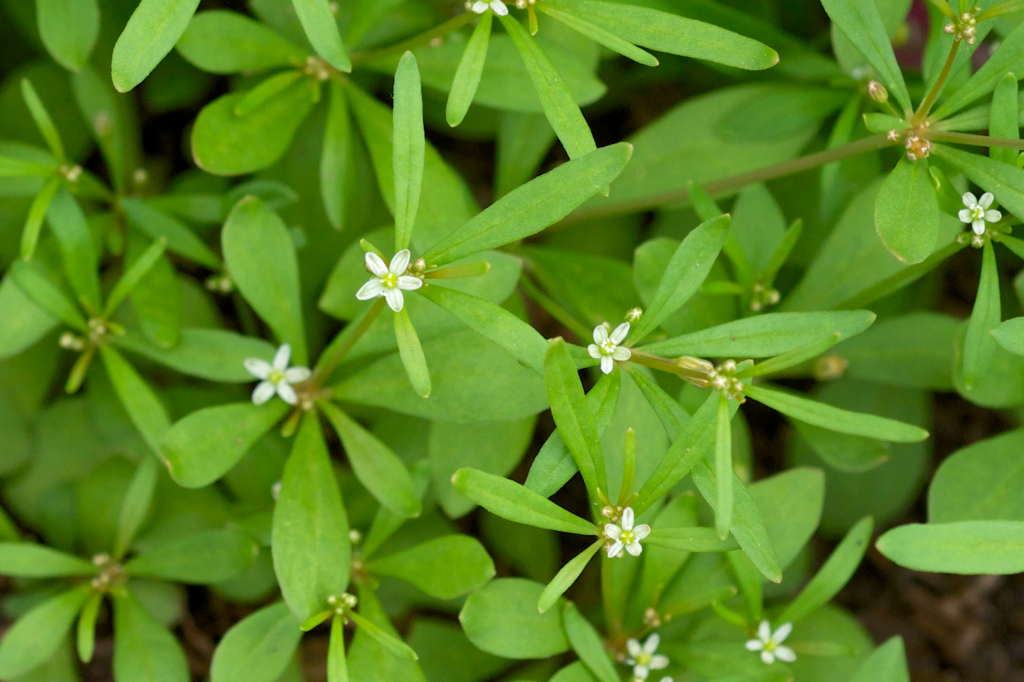

A summer annual weed with small white flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and glyphosate are effective in controlling carpetweed.
Creeping Charlie (Glechoma hederacea):
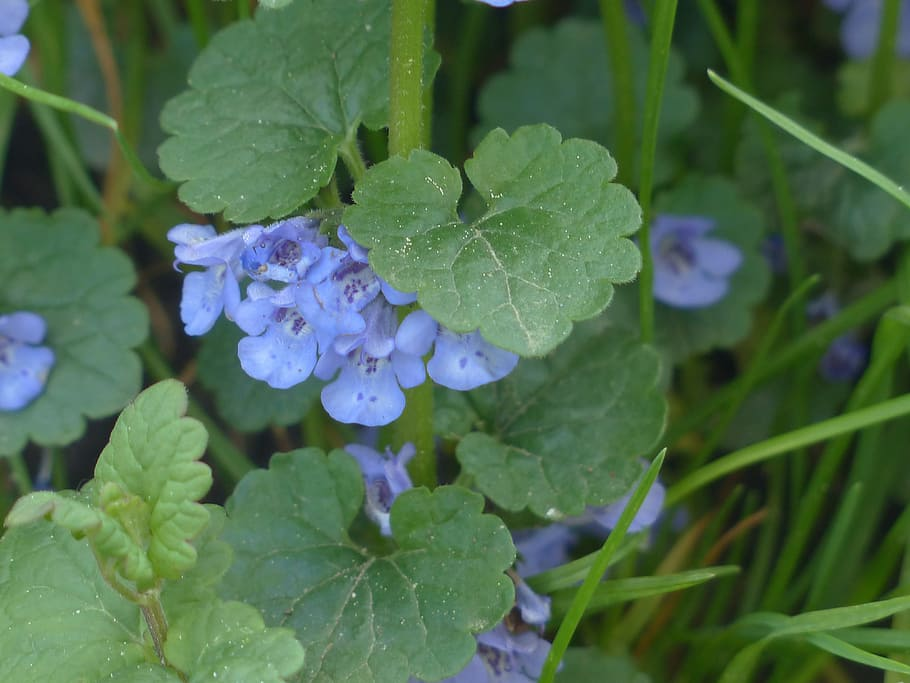

A perennial weed with a square stem that can smother other plants.
Herbicides such as dicamba, 2,4-D, and triclopyr are effective in controlling creeping Charlie.
Hairy bittercress (Cardamine hirsuta):
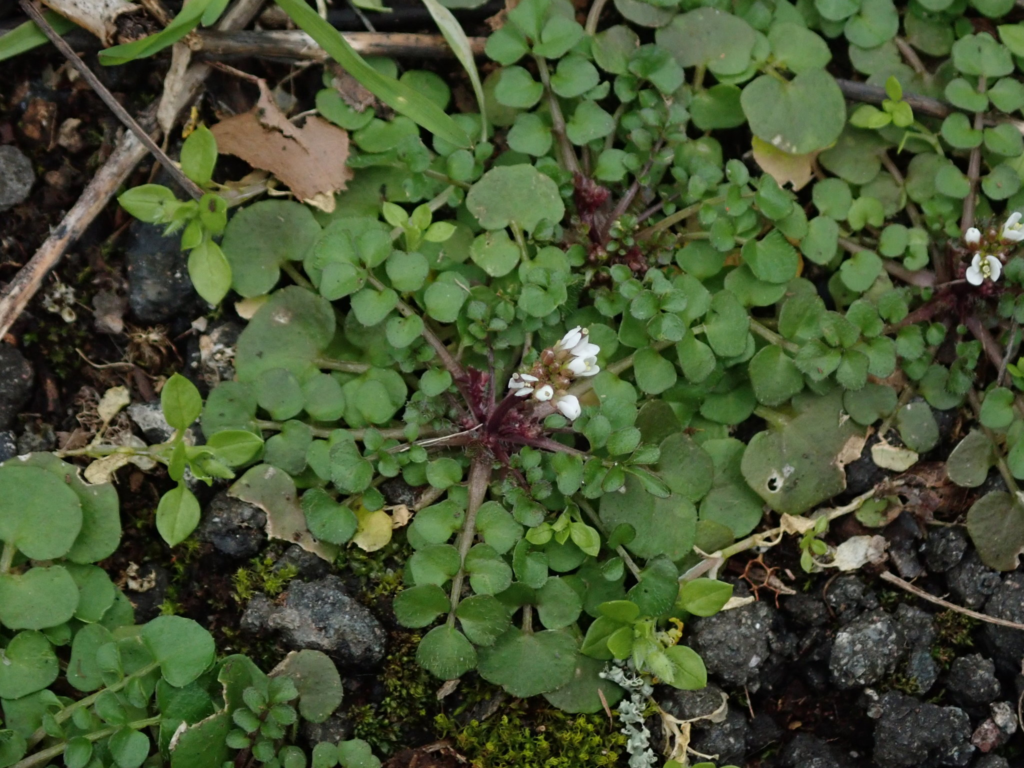

A cool-season annual weed with small white flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as glyphosate, 2,4-D, and dicamba are effective in controlling hairy bittercress.
Prostrate knotweed (Polygonum aviculare):
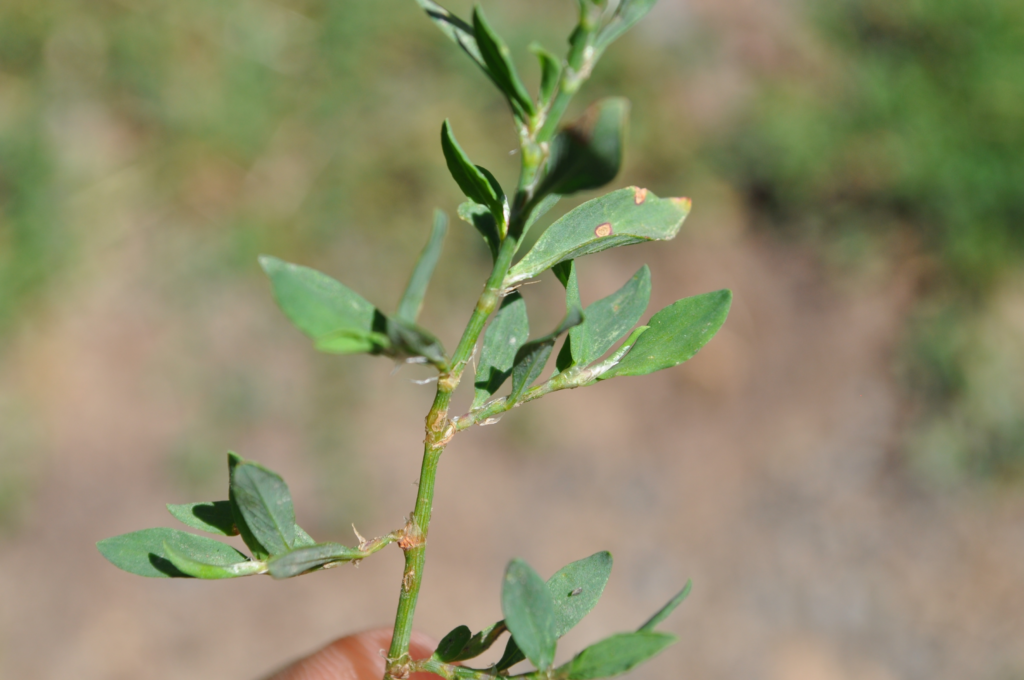

A summer annual weed with small pink flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds.
Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and glyphosate are effective in controlling prostrate knotweed.
Shepherd’s purse (Capsella bursa-pastoris):
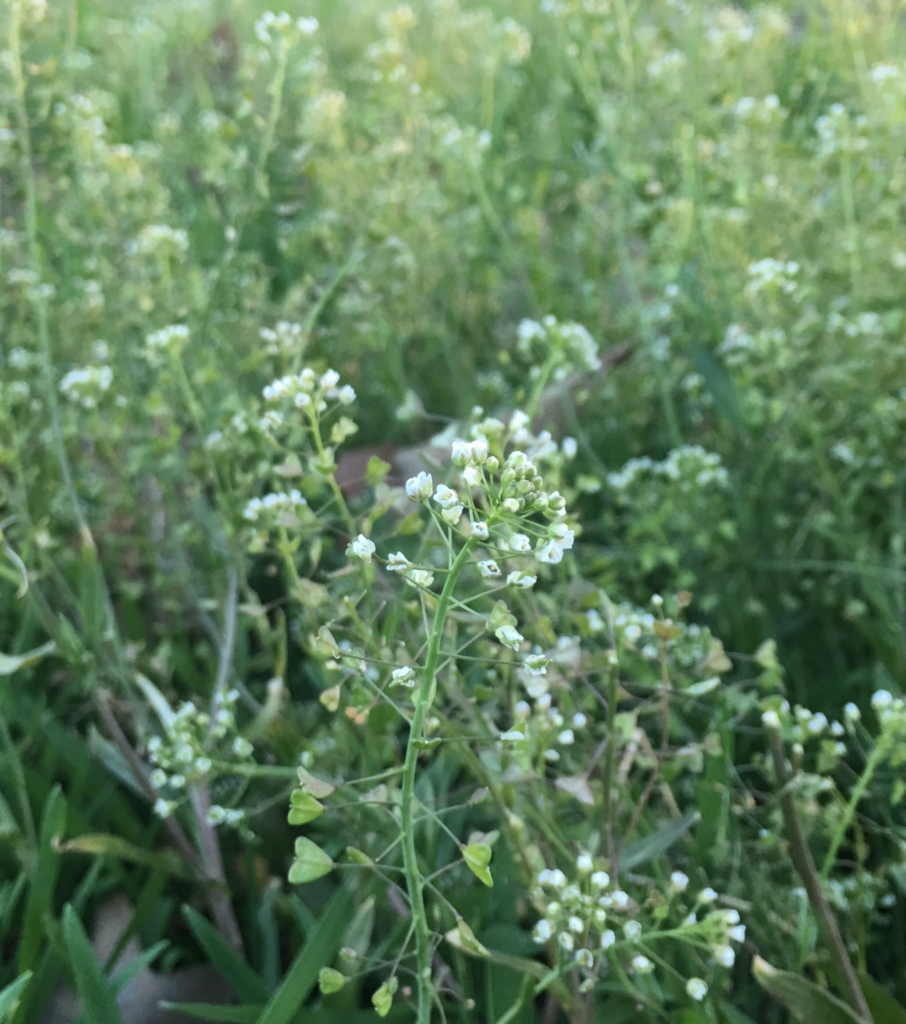

A cool-season annual weed with heart-shaped seed pods that can invade lawns and garden beds. Herbicides such as glyphosate, 2,4-D, and dicamba are effective in controlling shepherd’s purse.
Yellow wood sorrel (Oxalis stricta):

A perennial weed with clover-like leaves and yellow flowers that can invade lawns and garden beds. Herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and glyphosate are effective in controlling yellow wood sorrel.
Here are three herbicides that are effective in controlling a wide range of weeds:
Glyphosate:
A systemic herbicide that kills weeds by disrupting their ability to produce proteins.
It is effective against most broadleaf and grassy weeds, and is often used to control weeds in agricultural and non-agricultural settings.

2,4-D:
A selective herbicide that is commonly used to control broadleaf weeds in lawns, golf courses, and other turf areas.
It is effective against many common lawn weeds, including dandelions, clover, and thistle.

Dicamba:
A selective herbicide that is commonly used to control broadleaf weeds in agricultural and non-agricultural settings.
It is effective against many common weed species, including marestail, waterhemp, and pigweed.

commonly used organic herbicides:
Vinegar:
A solution of vinegar and water can be used to kill weeds.
It’s best used on small weeds as it may not be effective on larger ones.
Citric Acid:
A solution of citric acid and water can be used to kill weeds.
This method is effective on small weeds and has less impact on the environment than some other chemical herbicides.
Corn Gluten Meal:
This organic herbicide is a byproduct of the corn milling process.
It works by inhibiting the root development of weed seeds.
Essential Oils:
Essential oils such as clove oil, peppermint oil, and cinnamon oil can be used as organic herbicides.
They work by dehydrating the plant.

Salt:
Salt can be used as an herbicide, but it should be used with caution as it can affect soil quality and harm other plants.
It’s important to note that while organic herbicides may be safer for the environment than chemical herbicides, they can still harm beneficial plants and should be used with caution.
here are some general tips for using herbicides in a safe and responsible manner:
Read and follow the instructions on the herbicide label carefully, including any precautions or warnings.
Choose the right herbicide for the job.
Different herbicides are designed to target specific types of weeds, so make sure you select the appropriate one for the type of weed you are trying to control.
Apply herbicides when weather conditions are favorable.
Most herbicides work best when the temperature is between 60-85°F, and when there is no rain expected for 24-48 hours after application.
avoid using herbicides when it’s windy because the wind can carry the herbicide particles away from the target area, causing unintended damage to nearby plants.
Wind can cause the herbicide droplets to drift and spread over a larger area, potentially harming non-target plants, and exposing people and animals to harmful chemicals.
In addition, wind can make it difficult to control the amount of herbicide being applied, leading to over-application or uneven distribution.
This can result in the herbicide being less effective at controlling weeds, or causing damage to desirable plants.
Overall, it’s best to wait for a calm day with little to no wind to apply herbicides, to minimize the risk of unintended damage and ensure the herbicide is applied effectively.
Apply herbicides only to the areas where weeds are present, rather than applying them to the entire lawn or garden.
Avoid applying herbicides near water sources, such as streams or ponds, as they can contaminate these areas and harm aquatic life.
Store herbicides in a secure location, out of reach of children and pets.
Dispose of herbicides properly.
Do not pour leftover herbicide down the drain or into a storm drain.
Follow the disposal instructions on the label, or contact your local waste management facility for guidance.
You may also be interested in these articles:
- Slow-Release Fertilizers for Trees and Shrubs
- Fertilizing Flowers vs. Turf Nuances
- Fertilizing Flowers versus Vegetables in Your Garden
- Soil Testing, Crop Soil Testing, and Soil Sampling for Farmers
- DIY Soil Testing for Beginners
- Improving Soil Health with Green Manures
- Green Manures for Effective Weed Suppression
- Harnessing the Power of Green Manures to Enrich Sandy Soil
- Clay Soil Improvement
- Green Manures and their Environmental Impact
- Fertilizers for Plant Growth in Hydroponics
- Manure


